Your cart is empty
Subtotal:$0.00
In the intricate world of automotive engineering, every component plays a crucial role in ensuring safety, performance, and reliability. Among these components, brake rotors stand out as essential elements in a vehicle's braking system. Understanding the various types of brake rotors and choosing the right pattern is pivotal for optimizing braking performance. In this comprehensive guide on how to choose the right brake pattern, we will delve into the nuances of brake rotors, exploring the different types available and the factors to consider when making the right choice.

The Basics of Brake Rotors
Brake rotors, also known as disc brake rotors, are circular metal discs connected to the wheels of a vehicle. In vehicles equipped with a disc brake system, there can be up to four brake rotors, with one dedicated to each wheel. The primary function of brake rotors is to decelerate the rotation of the vehicle's wheels by leveraging friction. Working in tandem with brake calipers and brake pads, the braking process occurs when calipers squeeze the brake pads against the surface of the rotor, generating friction and effectively slowing down the wheel rotation and the vehicle's overall speed.
Types of Brake Rotors
Understanding the distinct types of brake rotors is essential for making an informed decision based on driving conditions, vehicle type, and personal preferences. The four primary types of brakes and rotors kit are:
1. Standard (Smooth) Rotors
Standard rotors feature a smooth, plain friction surface, making them the go-to design for most original equipment (OE) applications. These rotors are commonly found in factory-installed configurations and are suitable for various driving conditions. Standard rotors are cost-effective and provide a smooth and quiet braking operation when paired with quality disc brake pads.
2. Drilled Rotors
Drilled rotors are characterized by holes drilled into the friction surface of the disc. This design aids in heat dispersion, allowing for increased airflow through the disc and improved control of heat soak. While drilled rotors are effective at managing heat, they may wear unevenly and develop cracks, particularly in high-performance and racing applications. Special engineering of raw castings is necessary to maintain the integrity of the rotor casting during the drilling process.
3. Slotted Rotors
Slotted rotors feature narrow slots machined across the friction face of the disc. These rotors excel in heavy-duty applications or on competition vehicles. The slotted design enhances braking efficiency by reducing the build-up of gases and foreign deposits on the friction surface. This not only improves braking performance but also extends the lifespan of the brake system.
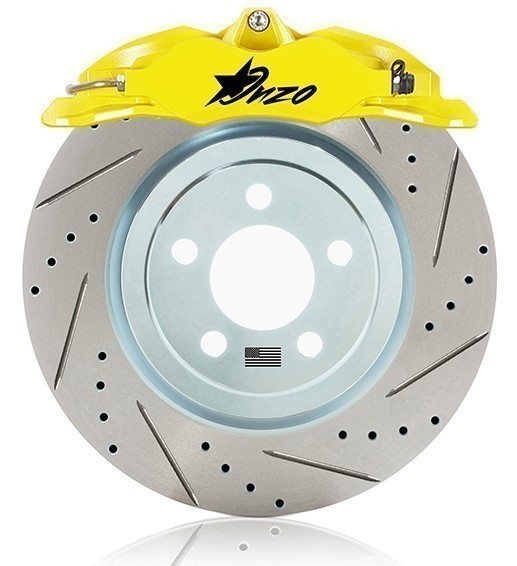
4. Drilled & Slotted Rotors
Combining the advantages and disadvantages of drilled and slotted designs, these rotors offer a comprehensive solution for high-performance applications or for those seeking aesthetic appeal. Drilled and slotted rotors are generally more expensive but deliver superior braking efficiency and are well-suited for performance-oriented driving.
Choosing the Right Brake Rotor
The choice of brake rotor depends on several factors, including driving conditions, vehicle type, and personal preferences. Here are key considerations:
Driving Conditions
Standard Rotors: Ideal for everyday driving conditions and general use.
Drilled Rotors: Suited for high-performance and racing applications with a focus on heat dispersion.
Slotted Rotors: Effective for heavy-duty driving conditions and competition vehicles, reducing gas build-up.
Drilled & Slotted Rotors: Best for performance enthusiasts seeking a balance between drilled and slotted advantages.
Vehicle Type
Standard Rotors: Suitable for most vehicle types, providing cost-effective performance.
Drilled Rotors: Best for high-performance and racing vehicles with special consideration for potential uneven wear.
Slotted Rotors: Recommended for heavy-duty vehicles and competition applications.
Drilled & Slotted Rotors: Ideal for performance-oriented vehicles where a combination of features is desired.
Personal Preferences
Standard Rotors: For those prioritizing cost-effective and reliable braking performance.
Drilled Rotors: Suited for enthusiasts seeking enhanced heat dispersion and a sporty aesthetic.
Slotted Rotors: Ideal for individuals looking for improved braking efficiency and durability.
Drilled & Slotted Rotors: Best for performance enthusiasts seeking a premium and versatile braking solution.
Brake Rotor Maintenance and Replacement
Brake rotors, like other wear-and-tear components, require periodic maintenance and eventual replacement. As the braking process wears down the steel friction surface of the rotors and brake pads, monitoring their condition is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Symptoms such as 'Disc Thickness Variation' (DVT) or 'shudder' may indicate the need for replacement. Once a rotor suffers from DVT, replacement becomes inevitable.
Brake rotors play a pivotal role in a vehicle's overall braking system, and choosing the right pattern is essential for achieving optimal performance. By understanding the characteristics of standard, drilled, slotted, and drilled & slotted rotors, drivers can make informed decisions based on their driving needs and preferences. Regular maintenance and timely replacement ensure the longevity and reliability of the braking system, contributing to safer and more enjoyable driving experiences.
If you want to choose the right brake pattern, do follow us at Braketime!
 Mar 27, 2024Unlocking the Benefits of Drilled and Slotted Rotors
Mar 27, 2024Unlocking the Benefits of Drilled and Slotted Rotors Mar 22, 2024Choosing The Right Brake Pad Kits For Your Vehicle: A Comprehensive Buyer's Guide
Mar 22, 2024Choosing The Right Brake Pad Kits For Your Vehicle: A Comprehensive Buyer's Guide Mar 18, 2024Exploring Different Types of Rear Brake Rotors
Mar 18, 2024Exploring Different Types of Rear Brake Rotors Mar 6, 2024Comparing Drilled vs. Slotted Disc Brake Rotors: Which Is Right for You?
Mar 6, 2024Comparing Drilled vs. Slotted Disc Brake Rotors: Which Is Right for You?
 Feb 5, 2024Comprehensive Guide on How To Check Brake Pads and Rotors for Optimal Maintenance
Feb 5, 2024Comprehensive Guide on How To Check Brake Pads and Rotors for Optimal Maintenance© 2023 - 2024 Braketimeusa. All rights reserved.
