Your cart is empty
Subtotal:$0.00
A vehicle’s braking system is crucial for ensuring the safety and performance of the driver and passengers. At the heart of this system lie the brake rotors, also known as brake discs, which play a pivotal role in bringing your vehicle to a halt. Understanding what brake rotors are, their importance, and how they function provides insight into the critical nature of regular brake system maintenance and the choice of rotor type for your vehicle.
Brake rotors are circular plates located within the wheel assembly. They work with the brake pads and calipers to slow down or stop the vehicle. When the brake pedal is pressed, the brake calipers squeeze the brake pads against the rotors, creating friction. This friction reduces the wheel’s rotation speed and, consequently, the vehicle’s speed.
The efficiency of a braking system largely depends on the condition and quality of its brake rotors. They provide the surface against which the brake pads press to create stopping power and play a crucial role in dissipating the heat generated by this process. Over time, wear and tear on the rotors can diminish their thickness and effectiveness, leading to longer stopping distances and potentially unsafe driving conditions. Therefore, understanding the different types of rear brake rotors available is essential for selecting the right kind for your vehicle’s specific needs and driving conditions.
The primary function of brake rotors is to convert the kinetic energy of the vehicle’s motion into thermal energy (heat) through friction. This process significantly reduces the vehicle’s speed, enabling it to stop. The generated heat is then dissipated into the atmosphere, preventing the braking system from overheating and maintaining efficiency. The ability of the rotor to absorb and dissipate this heat is a critical factor in its design and material composition. Different types of rotors offer varying degrees of heat dissipation, durability, and performance under stress, so choosing the right type of rear brake rotor is crucial for any vehicle.
Understanding the different types of brake rotors based on their construction is crucial for any vehicle owner or enthusiast. The brake rotor, an essential component of a vehicle’s braking system, comes in various types, each designed to suit specific driving conditions and vehicle types. This discussion delves into two primary types of brake rotors by construction: Solid/Non-Vented Brake Rotors and Vented Brake Rotors, highlighting their unique features, materials, and applications.
Solid or non-vented brake rotors are precisely as their name suggests: flat, smooth discs without any venting channels. These rotors are affixed directly to the vehicle’s rotating axle spindle, playing a crucial role in the vehicle’s ability to stop efficiently.
Description: These are uniform, solid discs that fit seamlessly within the wheel assembly. Their simplicity of design makes them a staple in many smaller vehicles.
Material: Solid brake rotors are typically made of iron, a material chosen for its durability and heat tolerance, albeit to a certain extent.
Characteristics:
Vented brake rotors are designed to address the heat dissipation challenges solid brake rotors face. These rotors feature gaps or spokes that allow air to flow through, significantly improving their ability to manage heat.
Description: Vented rotors consist of two rotor faces separated by vanes or vents. These vents create air channels that help expel heat more efficiently than solid rotors.
Heat Dissipation Mechanism:
When selecting brake rotors for a vehicle, understanding the rotor design or style differences is essential. These designs, which include Plain Faced/Smooth, Drilled, and Slotted brake rotors, offer varied benefits that cater to specific driving needs and preferences. Each type has unique features, from affordability and quiet operation to enhanced heat dissipation and improved braking performance.
Plain-faced or smooth brake rotors are the most common type in passenger vehicles. Their simplicity and effectiveness make them a preferred choice for everyday driving.
Features:
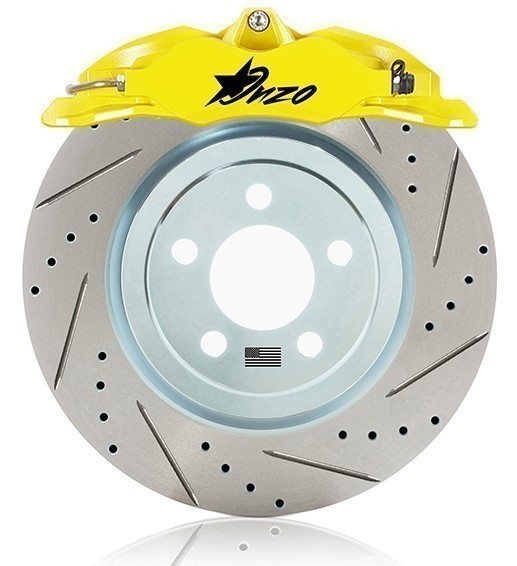
Drilled brake rotors feature holes around the metal surface, offering aesthetic appeal and functional benefits.
Drilled Holes Around the Metal Surface: The holes are strategically placed to improve the rotor’s ability to dissipate heat. This design allows hot gases released during braking to escape more easily, preventing heat buildup.
Aesthetic Appeal and Improved Heat Dissipation: Many drivers prefer drilled rotors for their sporty look. Beyond aesthetics, the improved heat dissipation helps maintain braking performance in demanding situations, such as during spirited driving or warmer climates.
Slotted brake rotors have long slots or lines etched into the metal surface, a design feature that enhances braking performance, especially under extreme conditions.
Long Slots or Lines in the Metal Surface: These slots serve a crucial purpose by allowing brake dust and gases to escape from the rotor surface, maintaining a clean contact area between the brake pad and the rotor.
Enhances Braking Performance and Reduces Brake Fade: The primary advantage of slotted rotors is their ability to enhance braking performance. The slots improve the rotor’s grip on the brake pads, resulting in quicker stops. They are particularly beneficial in preventing brake fade during heavy use, such as towing or racing, where the brakes are subjected to high-stress levels and heat.
Brake rotors are crucial components of a vehicle’s braking system, which convert kinetic energy into thermal energy through friction. The choice of materials used for brake rotors significantly impacts their performance, durability, and overall effectiveness. Understanding the properties of different rotor materials, including Cast Iron, Steel, and Layered Composite, is essential for selecting suitable rotors for specific driving conditions and vehicle types.
Cast iron is the most common material for brake rotors due to its excellent heat absorption capacity and durability.
Most Common Material: Cast iron rotors are widely used in vehicles of all types, from compact cars to heavy-duty trucks. Their prevalence is attributed to their reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Good Heat Absorption Capacity: Cast iron has a high thermal conductivity, allowing it to absorb and dissipate heat effectively during braking. This property helps prevent brake fade and ensures consistent braking performance, even under demanding driving conditions.
Steel brake rotors are lighter and thinner than cast iron rotors, making them suitable for specific applications where weight reduction is critical.
Lighter and Thinner than Cast Iron: Steel rotors, such as high-performance vehicles and racing cars, are favored in applications where reducing unsprung weight is desirable. Their lighter weight contributes to improved handling and acceleration.
Suitable for Specific Applications: While steel rotors offer advantages in weight reduction, they may have a different heat absorption capacity than cast iron rotors. Therefore, they are typically used in vehicles where extreme braking conditions are not a primary concern.
Layered composite rotors are innovative designs that combine different materials to achieve optimal performance and durability.
Combining Different Materials for Optimal Performance: Layered composite rotors feature a combination of materials, such as carbon fiber, ceramic, or reinforced metals, to maximize strength, heat dissipation, and wear resistance.
Enhanced Performance: By leveraging the unique properties of each material, layered composite rotors offer superior braking performance compared to traditional cast iron or steel rotors. They provide improved stopping power, reduced brake fade, and enhanced durability, making them ideal for high-performance vehicles and demanding driving conditions.
Understanding the different types of rear brake rotors is crucial as it empowers you to make informed decisions regarding the maintenance or upgrade of your vehicle’s braking system. With this knowledge, you can assess your vehicle’s needs and requirements, considering driving conditions, vehicle type, and personal preferences.
By understanding the nuances of rear brake rotors, you can confidently choose the most suitable options for your vehicle’s braking system. Whether performing routine maintenance or upgrading to enhance performance, this knowledge ensures that you invest in components that align with your vehicle’s requirements and driving habits. Ultimately, this empowers you to optimize your vehicle’s braking system’s safety, efficiency, and overall performance.
For more informative knowledge on brake rotors, visit us at Braketime today!
 Mar 27, 2024Unlocking the Benefits of Drilled and Slotted Rotors
Mar 27, 2024Unlocking the Benefits of Drilled and Slotted Rotors Mar 22, 2024Choosing The Right Brake Pad Kits For Your Vehicle: A Comprehensive Buyer's Guide
Mar 22, 2024Choosing The Right Brake Pad Kits For Your Vehicle: A Comprehensive Buyer's Guide Mar 18, 2024Exploring Different Types of Rear Brake Rotors
Mar 18, 2024Exploring Different Types of Rear Brake Rotors Mar 6, 2024Comparing Drilled vs. Slotted Disc Brake Rotors: Which Is Right for You?
Mar 6, 2024Comparing Drilled vs. Slotted Disc Brake Rotors: Which Is Right for You?
 Feb 5, 2024Comprehensive Guide on How To Check Brake Pads and Rotors for Optimal Maintenance
Feb 5, 2024Comprehensive Guide on How To Check Brake Pads and Rotors for Optimal Maintenance© 2023 - 2024 Braketimeusa. All rights reserved.
